Lyme disease, a complex and often misunderstood illness, has become one of the most prevalent vector-borne diseases in the Northern Hemisphere. Named after the town of Lyme, Connecticut, where it was first identified in the 1970s, this tick-borne disease affects hundreds of thousands globally each year. With its wide-ranging symptoms and controversial diagnostic and treatment protocols, Lyme disease has spurred intense scientific inquiry, patient advocacy, and public debate.
This comprehensive guide explores the origins, science, cases, treatments, notable controversies, famous cases, research advancements, and future direction of Lyme disease. It is designed to be informative, readable, and SEO-friendly—perfect for anyone seeking an in-depth look into this complex health condition.
What is Lyme Disease?
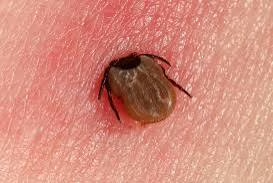
Lyme disease is an infectious disease caused by the Borrelia burgdorferi bacterium, primarily transmitted through the bite of infected black-legged ticks (commonly known as deer ticks). In Europe, other Borrelia species like Borrelia afzelii and Borrelia garinii are also responsible.
Transmission
Ticks become infected by feeding on small mammals like mice, and then transfer the bacteria to humans through bites. A tick usually needs to be attached for 36-48 hours to transmit the bacterium effectively.
Symptoms
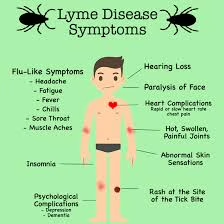
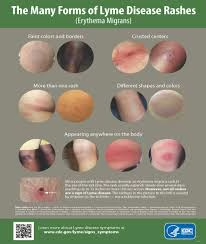


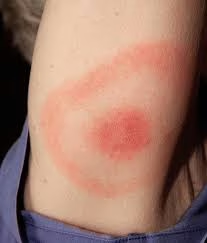
Symptoms can be classified into three stages:
- Early Localized Stage:
- Erythema migrans (EM) or “bull’s-eye” rash
- Fever, chills, fatigue, headache, muscle and joint aches
- Early Disseminated Stage:
- Multiple rashes
- Neurological symptoms (e.g., facial palsy, meningitis)
- Heart palpitations or Lyme carditis
- Late Disseminated Stage:
- Arthritis (especially in large joints like knees)
- Persistent neurological issues (e.g., memory loss, neuropathy)
The History of Lyme Disease
Origins
Though first identified in 1975 in Lyme, Connecticut, retrospective studies suggest Lyme disease existed long before that. The 5,300-year-old mummy known as Otzi the Iceman tested positive for Borrelia burgdorferi, making it one of the oldest known cases.
Timeline of Key Events
- 1975: Cluster of arthritis-like cases in children in Lyme, Connecticut
- 1981: Willy Burgdorfer discovers Borrelia burgdorferi
- 1990s-2000s: Rising awareness, controversies over chronic Lyme
- 2000s-present: Explosive growth in cases and research
Epidemiology: How Widespread is Lyme Disease?
Global Distribution
- United States: Most cases occur in the Northeast, Midwest, and Pacific Northwest
- Europe: Widespread, particularly in Central and Eastern Europe
- Asia: Cases reported in China, Japan, Russia
Statistics
- Estimated 476,000 Americans diagnosed and treated annually
- Underreporting is common due to misdiagnosis or lack of recognition
Climate Change and Spread
Warmer temperatures and changing ecosystems are expanding tick habitats, potentially increasing future incidence.
Diagnosis and Testing
Current Methods
- Clinical Diagnosis: Based on symptoms and history of tick exposure
- Laboratory Tests:
- ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay)
- Western Blot test
Limitations
- Early tests may return false negatives
- Chronic or late-stage Lyme often remains undetected
Treatment Protocols
Antibiotics
- First-line Treatment: Doxycycline, amoxicillin, or cefuroxime for 2-4 weeks
- Severe Cases: IV antibiotics like ceftriaxone
Controversy Over Chronic Lyme Disease
Some patients report persistent symptoms after standard treatment, often referred to as Post-Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome (PTLDS). This condition is controversial:
- Mainstream Medicine: Suggests persistent symptoms are not due to active infection
- Alternative Views: Advocate for long-term antibiotic therapy
Complementary Treatments
- Herbal medicine
- Nutritional therapy
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
Scientific Research and Developments
Vaccines
- LYMErix: Withdrawn in 2002 due to low sales and controversy
- Valneva’s VLA15: Currently in Phase 3 trials with Pfizer
Genomics and Diagnostics
- Advances in genome sequencing of Borrelia strains
- Development of more sensitive diagnostics using CRISPR and AI
Biofilm and Persistence
Studies suggest Borrelia can form biofilms, making it harder to eradicate, and may exist in persistent forms undetectable by conventional tests.
Famous Cases
Yolanda Hadid
The former supermodel and reality star has publicly battled chronic Lyme, raising awareness through her platform.
Avril Lavigne
The pop singer revealed her struggle with Lyme disease, describing it as “the worst time of my life.”
Alec Baldwin’s Wife, Hilaria Baldwin
She also shared her chronic Lyme experience, emphasizing the need for greater understanding and support.
Success Stories and Treatment Failures
Successes
- Early diagnosis and prompt antibiotic treatment often lead to full recovery
- Clinical studies demonstrating remission with combination therapies
Failures
- Misdiagnosis as fibromyalgia, MS, or psychiatric illness
- Late diagnosis resulting in irreversible neurological damage
- Lack of standardized treatment for chronic or persistent Lyme
Doctors and Advocates
Notable Doctors
- Dr. Richard Horowitz: Known for the “MSIDS model” (Multiple Systemic Infectious Disease Syndrome)
- Dr. Joseph Burrascano: Pioneer in chronic Lyme treatment protocols
- Dr. Neil Spector: Cardiologist and Lyme sufferer who advocated for better diagnostics
Patient Advocates
- LymeDisease.org
- Global Lyme Alliance
- Bay Area Lyme Foundation
The Future of Lyme Disease
Promising Areas of Research
- Vaccines: Second-generation options may hit the market in coming years
- Nanotechnology: For targeted antibiotic delivery
- Artificial Intelligence: Improving diagnostic accuracy
Public Health Initiatives
- Tick surveillance programs
- Public education on prevention
- Environmental controls like deer population management
Policy and Legislation
- The 21st Century Cures Act allocated funding for tick-borne disease research
- Advocacy for insurance coverage of long-term treatments
SEO-Optimized Key Takeaways
- What is Lyme disease? A tick-borne illness caused by Borrelia bacteria
- Lyme disease symptoms: Rash, fatigue, joint pain, neurological issues
- How do you get Lyme disease? From black-legged tick bites
- Is Lyme disease curable? Often, but chronic cases remain controversial
- Famous Lyme cases: Yolanda Hadid, Avril Lavigne, Hilaria Baldwin
- Best Lyme disease treatments: Antibiotics, herbal support, lifestyle changes
- Future of Lyme research: Vaccines, AI diagnostics, precision medicine
Conclusion
Lyme disease is a multifaceted illness with a history rooted in both science and controversy. It spans centuries and affects hundreds of thousands each year. Despite advancements, challenges in diagnosis, treatment, and public awareness persist. With continued research and advocacy, the future holds promise for improved care, clearer guidelines, and ultimately, hope for those affected.
Stay informed. Stay protected. And always check for ticks.
